1. Hedge accounting: fair value hedge using an interest rate swap
In the example of hedge accounting in the chapter, the borrower, Bottom, swaps floating payments for fixed ones to hedge fluctuations in interest rates and therefore in its cash flows. But what if Bottom swaps fixed payments for floating ones? In this case, it’s the fair value of the debt that is being hedged since the value of fixed-rate debt is sensitive to interest rate changes. The key facts of Bottom’s new interest rate swap are summarised below.
At start-x1, Bottom borrows ![]() 10 million from G.W. Capital for three years at a fixed rate of 7%. Interest is paid annually. Bottom enters into a swap contract with Wild Thyme Bank on the same date. Under the swap Bottom pays interest at a floating rate equivalent to Euribor and receives interest at a fixed rate of 7%. The swap has a notional principal of
10 million from G.W. Capital for three years at a fixed rate of 7%. Interest is paid annually. Bottom enters into a swap contract with Wild Thyme Bank on the same date. Under the swap Bottom pays interest at a floating rate equivalent to Euribor and receives interest at a fixed rate of 7%. The swap has a notional principal of ![]() 10 million and a three-year term and the variable interest rate is reset annually.
10 million and a three-year term and the variable interest rate is reset annually.
Annual swap receipts and payments – and end-year fair values of the swap contract – in the three years x1–x3 are set out below. (Currency amounts are in euros.)
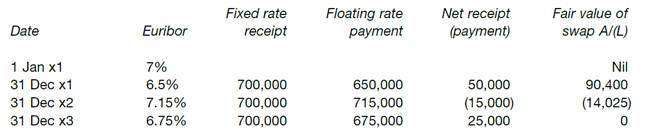
Bottom designates changes in the fair value of the swap as a hedge of changes in the fair value of the debt due to changes in Euribor. Under IAS 39, the swap contract must be separately recognized and measured at its fair value. (Initially, this is zero as the Euribor rate is 7% at the start of x1.) The carrying amount of the loan is also adjusted for changes in its fair value due to changes in Euribor. All gains and losses are recognised in the income statement.
Required
Show the entries Bottom must make in its accounts to record the loan payments and the changes in fair values of both swap and loan over the three years x1–x3. What is the net cost of the loan to Bottom in each of the three years?